Toxic Heavy Metals and Chelation Therapy
Heavy metals can be toxic and necessary for human health and life. Nutrients like cobalt, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, selenium, and zinc are heavy metals that are necessary in small amounts. There are 35 heavy metals that health officials have identified as dangerous to human health. The most problematic are toxic heavy metals like lead, mercury, arsenic (metalloid), cadmium, thallium, and aluminum. The term “heavy” describes these metals and metalloids because they have a high atomic weight and density as compared to water.
Humans accumulate toxic heavy metals through the skin, inhalation, and ingestion from food, air, and water. Primary sources include contaminated soil, rainwater, waterways, manufacturing emissions, chemical spills, dental fillings, home and business construction materials, cigarette smoke, and fireworks. Common everyday items like medications, dietary supplements, personal care products, cosmetics, paint, batteries, lightbulbs, gasoline, lawn pesticides, and fungicides are known sources of toxic heavy metals.
What Does Heavy Metal Exposure Do to the Body?
We cannot escape exposure to toxic heavy metals, but reducing exposure is essential. One’s risk of toxicity depends on many factors, one or more factors, including age, body weight, genetics, route of acquisition, duration and amount of exposure, overall health, and nutritional status.
Children are at greater risk for toxicity from heavy metals than adults because of body weight and the way their bodies metabolize heavy metals.
Heavy metal toxicity can lower energy levels and damage the functioning of the brain, lungs, kidneys, liver, heart, and blood composition. Chronic conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can be linked to exposure to toxic heavy metals and other environmental chemicals. Studies show that long-term exposure can lead to gradually progressive physical, muscular, and neurological degenerative processes, which mimic multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and muscular dystrophy. Some cancers are also linked to long-term exposure to metals and their compounds. What can make things worse is a negative synergetic effect for some individuals with other issues, such as Lyme disease, mold exposure, and genetic predisposition. So, there is a need to address each patient individually. For these reasons, if you believe you have been exposed to heavy metals, you must seek medical help from physicians trained to treat heavy metal toxins.
How Is Heavy Metal Exposure Diagnosed?
The National Institutes of Health reports that heavy metal toxicity is underdiagnosed and that when a person has multiple exposures, diagnosis is highly complex because symptoms vary. The symptoms are often vague and could describe a host of other common conditions and the way their bodies metabolize heavy metals.
Heavy metal toxicity can lower energy levels and damage the functioning of the brain, lungs, kidneys, liver, heart, and blood composition. Chronic conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can be linked to exposure to toxic heavy metals and other environmental chemicals. Studies show that long-term exposure can lead to gradually progressive physical, muscular, and neurological degenerative processes, which mimic multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and muscular dystrophy. Some cancers are also linked to long-term exposure to metals and their compounds. What can make things worse is a negative synergetic effect for some individuals with other issues, such as Lyme disease, mold exposure, and genetic predisposition. So, there is a need to address each patient individually. For these reasons, if you believe you have been exposed to heavy metals, you must seek medical help from physicians trained to treat heavy metal toxins.
How Is Heavy Metal Exposure Diagnosed?
The National Institutes of Health reports that heavy metal toxicity is underdiagnosed and that when a person has multiple exposures, diagnosis is highly complex because symptoms vary. The symptoms are often vague and could describe a host of other common conditions and environmental exposures like mold toxicity. Experts are only beginning to understand better how these toxins affect overall human health and longevity.
The clinical manifestations of toxic heavy metals may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Autoimmune disorders
- Brain fog, confusion, and memory loss
- Cardiovascular issues
- Chills
- Depression, mood, or behavior changes
- Digestive problems and inflammation
- Fatigue
- Hair and skin changes
- Headaches
- High or low blood pressure
- Joint pain
- Kidney problems
- Metabolic and blood sugar disorders
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Shortness of breath
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches for Heavy Metal Toxicity at Restoration Healthcare
Once a diagnosis is certain, numerous treatments will be prescribed. At Restoration Healthcare, our doctors use an integrative approach to treating heavy metal toxicity, considering personal health history and existing condition(s). A physician will do a thorough workup to include specific testing of the neurologic systems, which is the most sensitive system affected by heavy metal toxicity. We work closely with each patient to develop a personalized approach that addresses diet, exercise, stress management, and nutritional supplements.
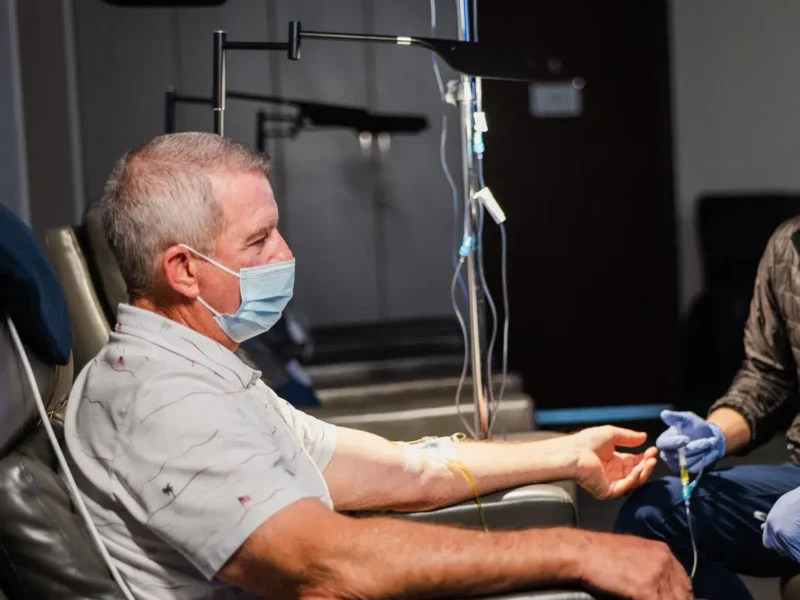
Chelation intravenous therapy is a primary treatment method to aid the body in ridding it of toxins. Chelation therapy uses compounds that bind with heavy metals and allows the body to eliminate toxins. The term chelation means to bond. The most effective chelation therapies are delivered through the bloodstream in an intravenous IV Therapy drip.
The most common chelating agents include dimercaprol, DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid), and CaEDTA (calcium ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid). At Restoration Healthcare, we prefer CaEDTA because heavier metals, such as lead and mercury, have a greater affinity for EDTA and form stronger bonds. Our trained IV therapists administer a prescribed dose of CaEDTA, which attaches to heavy metal toxins and certain minerals and forms chemical compounds called chelates. The chelates travel through the blood to the kidneys, filtered and excreted in the urine.
If you suspect you have been exposed to heavy metal toxins affecting your health, you must get medical help. You may be tempted to use a home detox plan, but this severe health issue needs medical supervision and guidance. Whether your symptoms are related to heavy metal toxicity or something else entirely, Restoration Healthcare will investigate and provide you with an integrative healthcare plan to help restore your body to health.
FAQs:
1. What is chelation therapy?
Chelation therapy is a treatment that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals and toxins from the body. It is often delivered through intravenous (IV) therapy.
2. How does chelation therapy work?
Chelating agents, such as CaEDTA, bind with heavy metals like lead and mercury, forming compounds that are then filtered through the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
3. What are the most common chelating agents used in therapy?
Common chelating agents include dimercaprol, DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid), and CaEDTA (calcium ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid). At Restoration Healthcare, we primarily use CaEDTA for its effectiveness in binding with heavy metals.
4. Is chelation therapy safe?
Chelation therapy is generally safe when administered by trained healthcare professionals. It is important to undergo this treatment under medical supervision to avoid potential complications.
5. What are the symptoms of heavy metal toxicity?
Symptoms of heavy metal toxicity can vary but may include fatigue, headaches, digestive issues, cognitive difficulties, and muscle pain. If you suspect exposure, it’s important to seek medical advice.

