How NAD+ Seeks to Slow and Reverse the Aging Process
Many of us aren’t so much afraid of dying as we are afraid of aging. We fear losing our youthful vigor and appearance, our mental acuity, and our freedom as we gradually rely more and more on others.
In a perfect world, we would all age gracefully — body and mind intact, healthy, fit, and energetic until the day we die — hopefully in our sleep. We know it’s possible. We’ve seen it happen — people living to 100 and beyond and living well. They’re not winning marathons or competing in the Olympics, yet they are maintaining both hope and quality of life.
We often attribute the ability to age gracefully to “good genes,” and genes certainly play a role in health, fitness, and the aging process. Unfortunately, we can’t replace the genes we inherited — but what if we could support the genes we have and reverse the damage to those genes that typically occurs over time? If we could do that, we may be able to restore health at the cellular level, essentially turning back the clock on the aging process.
This may sound like a pipe dream. After all, human beings have been searching for the Fountain of Youth at least as far back as Alexander the Great (356 to 323 BCE). We have yet to discover a place of healing water or a magic elixir, but we are getting closer as we come to understand more about the aging process and begin to identify key factors that play a role in it.
Of course, we’re already aware of the importance of proper nutrition and staying active — physically, mentally, and socially. But we’re still in the early stages of identifying and developing anti-aging extracts or pharmaceuticals. Currently, some of the most promising solutions are coming from research into NAD+ and sirtuins.
Understanding NAD+: A Vital Cofactor
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a chemical compound present in every living cell, where it functions as an essential cofactor — a substance that other enzymes need in order to do their jobs. It was discovered in 1906. Since then, a growing body of research has come to show that NAD+ plays a critical role in maintaining cellular health.
As we age, NAD+ gradually declines, and low levels of NAD+ have been shown to contribute to a variety of age-related diseases, including cognitive decline, cancer, metabolic disease, and sarcopenia (loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength). In other words, declining NAD+ isn’t just a symptom of aging — it causes aging.
The body produces NAD+ in the following ways:
- Through the de novo synthesis pathway, creating it from scratch using L-tryptophan (an amino acid in turkey, milk, and whole grains)
- Through the Preiss-Handler pathway, using dietary nicotinic acid and the enzyme nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT)
- Through the “salvage pathway,” which recycles NAD+ from chemical precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
The first two pathways require multiple steps to produce NAD+. The third is streamlined, allowing for a rapid increase of NAD+ levels with the administration of supplemental NR or NMN. NMN has the added benefit of having a dedicated transporter in cell membranes that carries it directly into cells, where it’s converted into NAD+.
NAD+ and Sirtuins — Longevity Proteins
As a cofactor, one of NAD+’s most essential roles is serving as a coenzyme for sirtuins — a group of proteins that promote longevity. Sirtuins regulate histone deacetylation — a process that removes small chemical groups (acetyls) from proteins called histones. Histones are spherical proteins around which DNA is wrapped inside the nucleus of each cell. This process promotes genome stability, ensuring correct gene expression, which helps to slow the aging process.
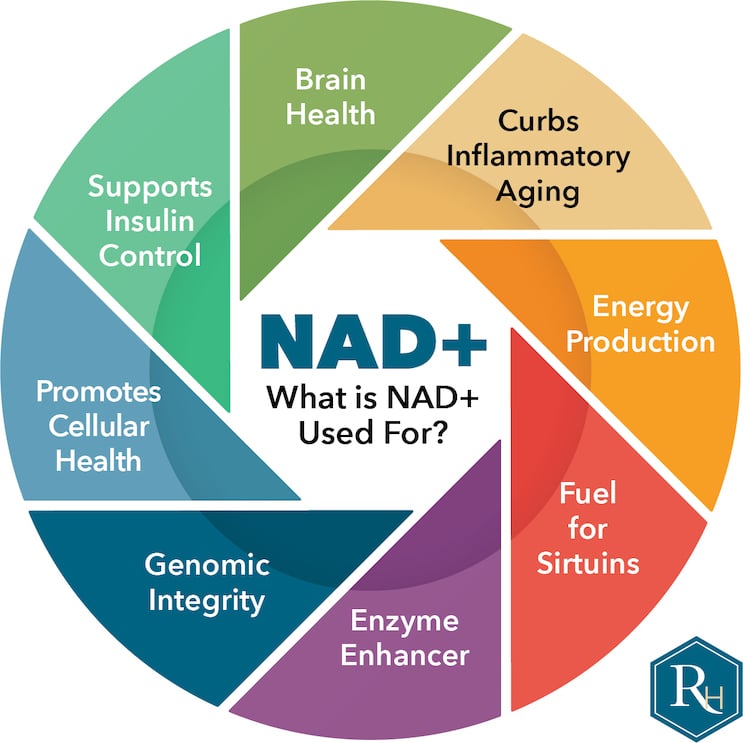
NAD+, alone and in combination with sirtuins, delivers several anti-aging benefits, including the following:
- Supports overall health: NAD+ provides the fuel for sirtuins, which play a key role in numerous physiological processes for maintaining health and vitality.
- Supports healthy inflammatory response and curbs inflammaging: Inflammaging (short for “inflammatory aging”) is chronic low-grade inflammation believed to accelerate the aging process. NAD+ is essential for producing two proteins that support a healthy inflammatory response and help to slow the progression of inflammaging — sirtuins and CD38 (also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase).
- Sirtuins help to control the production of NFκB, which is involved in the production of cytokines— inflammatory molecules involved in the immune response.
- CD38 is a glycoprotein on the surface of many immune cells that also supports a healthy inflammatory response.
- Supports insulin control and energy production at the cellular level: Sirtuins help to control the production of PGC-1α — a protein involved in insulin signaling and mitochondrial biogenesis, the process that increases the number and size of mitochondria (the energy generators in cells).
- Improves the body’s ability to repair DNA and supports genomic integrity: NAD+ is a cofactor for a family of enzymes involved in DNA repair, the maintenance of genomic integrity, and programmed cell death.
- Helps regulate circadian rhythm to enhance restorative sleep: Circadian rhythm is the 24-hour sleep-wake cycle controlled by the biological clock in the body. It plays a key role in the production of NAMPT, the enzyme that creates NAD+ from vitamin B3. Restoring healthy NAD+ levels may support the body’s circadian rhythm, resulting in the production of additional NAD+.
How to Support NAD+ Production and Sirtuin Activity
Now that you have an inkling about the anti-aging benefits of NAD+ and sirtuins, you’re probably wondering how to boost your levels of these substances in your body. Here are five great ways to start:
- Practice intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting involves going without food for extended periods of time on a regular basis. Many people choose to fast for 12 to 14 hours daily. An example would be not eating from 8 p.m. until 8to 11 a.m. (or later) the next day. A growing body of research links intermittent fasting with numerous health benefits, including weight loss, healthy blood pressure, lower cholesterol, and improved blood-sugar regulation. It’s also a great way to support sirtuin activity. (For information on intermittent fasting, we recommend reading Understanding the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting and Living Healthy in a Toxic Environment — Part III, Food and Fasting, both of which are available here on the Restoration Healthcare blog. If you’re a Restoration Healthcare patient, use your OnPatient Portal account to request your own copy of Fasting 101: A Restoration Healthcare Primer on Medically- supervised Fasting.)
- Combine aerobic exercise with resistance or weight training. Exercise increases the expression of sirtuins and promotes the production of healthy mitochondria, thereby increasing ATP production to energize cells.
- NAD+ IVs and nasal sprays: Talk to your Restoration Healthcare doctor about NAD-containing IVs and nasal sprays.
- Take a quality oral NMN supplement. NMN is a key ingredient your body can access quickly and directly to replenish NAD+ levels and support sirtuin activity.
- Take a sirtuin-activating compound (STAC). STACs include resveratrol (present in grapes and red wine) and Quercetin, which has milder effects than resveratrol. However, Quercetin offers multiple health benefits, including promoting metabolic health, reducing inflammation, dampening mast cells, and serving as an antioxidant.
Keep in mind that health and fitness require more than just a healthy diet, regular exercise, and a couple of supplements. Your body may be low in one or more essential nutrients it needs for optimal function, or you may have a hidden infection or toxic load that’s holding you back. The only way to figure out what’s going on beneath the surface is through testing and consulting with a doctor who has a deep understanding of how the body functions at both a systems and cellular level.
– – – – – – – – – – – –
Disclaimer: The information in this blog post about nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is provided for general informational purposes only and may not reflect current medical thinking or practices. No information contained in this post should be construed as medical advice from the medical staff at Restoration Healthcare, Inc., nor is this post intended to be a substitute for medical counsel on any subject matter. No reader of this post should act or refrain from acting on the basis of any information included in, or accessible through, this post without seeking the appropriate medical advice on the particular facts and circumstances at issue from a licensed medical professional in the recipient’s state, country or other appropriate licensing jurisdiction.